Software as a medical device (SaMD) refers to software designed for medical purposes. These can include mobile apps, clinical decision support systems, and medical image analysis software, among others. To ensure the safety and efficacy of Software as a medical device (SaMD), government agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) require that SaMD undergoes a clinical evaluation.
We have written a detailed blog on SaMD that discusses the eligibility, origin, classification, expected growth, and many other aspects of Software as a Medical Device.
But in this blog, we will discuss a very specific topic of SaMD. Here we will analyze all aspects of Software as a medical device (SaMD) clinical evaluation.
In addition to reading, you can watch this blog about Software as a medical device clinical evaluation too!
FDA released a guidance document on this subject back in 2017, please check it here.
Clinical evaluation is the process of assessing the clinical performance and safety of SaMD. Basically, it involves identifying the intended use of the software, determining the clinical benefits and risks associated with the software, and conducting clinical studies to evaluate the performance of the software in a clinical setting.
The Importance of Software as a medical device (SaMD) clinical evaluation
Clinical evaluation is crucial for ensuring that SaMD is safe and effective. By evaluating the clinical performance and potential risks of SaMD, clinical evaluation helps to protect patients. Additionally, it ensures that the patients receive the best possible care.
Clinical evaluation is also important for gaining regulatory approval. SaMD must obtain regulatory approval from agencies like the FDA and EMA before healthcare providers buy it. The regulatory approval process includes clinical evaluation, which is a crucial component of demonstrating the safety and efficacy of the software.
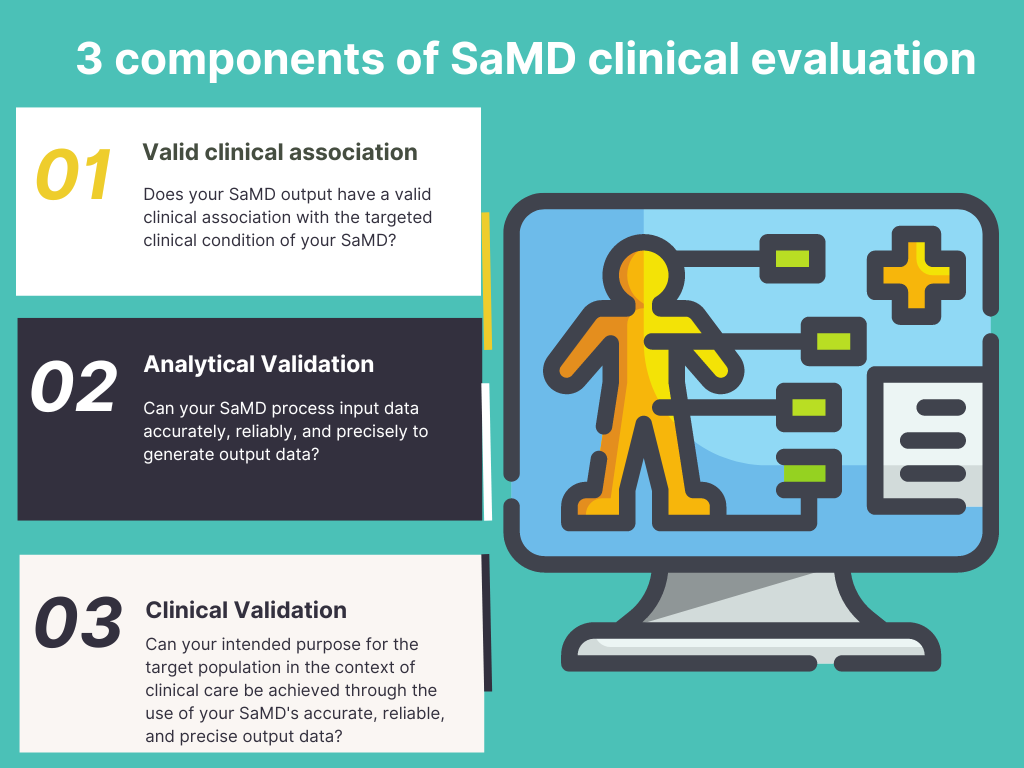
Three important components of SaMD clinical evaluation
Basically, the Clinical Evaluation of SaMD has mainly three key components. They are,
Valid clinical association
Does your SaMD output have a valid clinical association with the targeted clinical condition of your SaMD?
Analytical Validation
Can your SaMD process input data accurately, reliably, and precisely to generate output data?
Clinical Validation
Can your intended purpose for the target population in the context of clinical care be achieved through the use of your SaMD’s accurate, reliable, and precise output data?
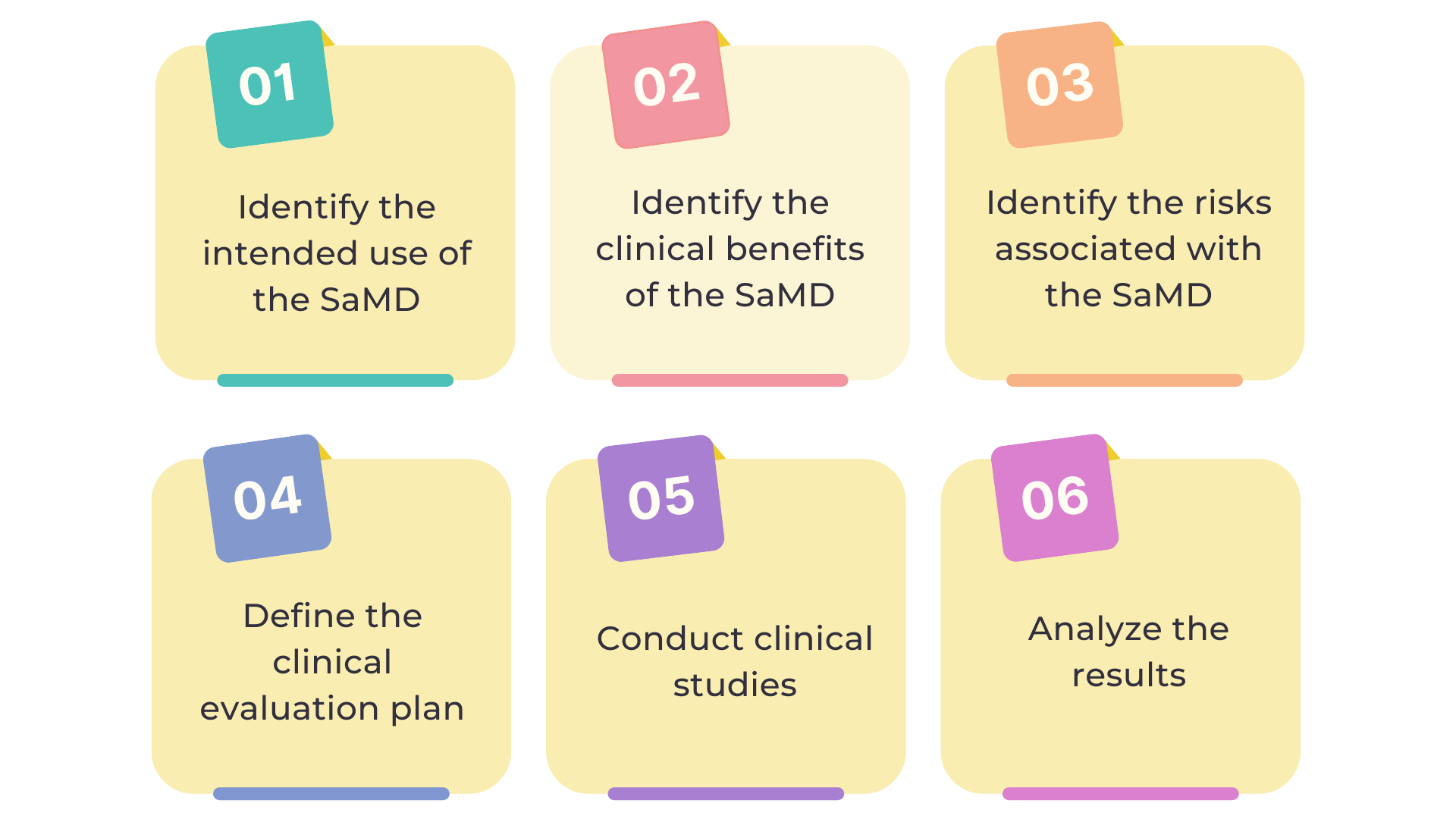
Steps Involved in Software as a medical device (SaMD) clinical evaluation
Furthermore, there are several steps in SaMD clinical evaluation:
Identify the intended use of the SaMD
The first step in SaMD clinical evaluation is to identify the intended use of the software. This involves defining the medical condition that the software is intended to diagnose, treat, or prevent, as well as the patient population for which the software is intended.
Identify the clinical benefits of the SaMD
The next step is to identify the clinical benefits of the SaMD. This involves determining how the software will improve clinical outcomes. Some examples would be, improving patient outcomes, reducing the risk of adverse events, or increasing efficiency in the clinical setting.
Identify the risks associated with the SaMD
The third step is to identify the risks associated with the SaMD. This involves assessing the potential risks associated with the use of the software. Some examples would be, misdiagnosis, inaccurate data analysis, or incorrect treatment recommendations.
Define the clinical evaluation plan
After identifying the intended use, clinical benefits, and risks associated with the SaMD, the next step is to define the clinical evaluation plan. The plan outlines the methodology for evaluating the clinical performance of the software and identifying any potential risks.
Conduct clinical studies
The next step is to conduct clinical studies to evaluate the clinical performance of the SaMD. The type and size of the study will depend on the intended use of the software, the clinical benefits and risks, and the regulatory requirements.
Analyze the results
The final step is to analyze the results of the clinical studies. Comparing the clinical performance of the software to the intended use, clinical benefits, and risks outlined in the clinical evaluation plan is essential. After conducting the comparison, the analysis results are then utilized to determine if the software is safe and effective for use in clinical settings. The analysis results are also used to assess whether the software meets the regulatory requirements for marketing and sale.
Conclusion
SaMD is an important and growing area of medical technology, with the potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery. However, we must subject SaMD to rigorous clinical evaluation to ensure that it is safe and effective. Clinical evaluation is a crucial component of the regulatory approval process for SaMD. It involves identifying the intended use, clinical benefits, and risks of the software. Clinical studies are conducted to evaluate the performance of the software. The objective of clinical evaluation is to ensure that SaMD is safe and effective. The evaluation process helps to protect patients and improve the quality of healthcare delivery.