In order to navigate the complex manufacturing maze, the idea of a manufacturing traveler is useful. In this blog, we will discuss what a manufacturing traveler is, why it matters, and how document management software may transform the manufacturing industry.
Now You Can Watch This Blog About Manufacturing Traveler Too!
Manufacturing Process Complexity:
Planning, production, quality assurance, and distribution are just a few of the different processes that make up the multidimensional field of manufacturing. It is a difficult task to guarantee a smooth operation flow while keeping consistent quality across many batches. Complex workflows, strict regulatory constraints, and a perpetual need for innovation must all be managed by manufacturers.
Consistency is not simply a virtue, it is a need in the industrial industry. A systematic method is necessary to guarantee that every batch of items complies with the same high standards. The manufacturing traveler comes into play in this situation.
Manufacturing Traveler: Establishing the Production Compass
A manufacturing traveler is a thorough document that follows a product throughout its manufacturing process. It is also known as a production traveler or work order traveler. Each step of the production process is described, including the selection of raw materials, assembly, quality assurance, testing, and packing. This manual serves as a road map, directing personnel, managers, and quality assurance teams to ensure compliance with specified standards.
Manufacturing Traveler: Examples for Different Industries
Let’s look at a few instances of manufacturing traveler from other sectors of the economy:
Automotive Industry: A production traveler for an automobile engine can include information on the details of each component, instructions for assembly, bolt torque specifications, and quality control checkpoints.
Pharmaceutical Industry: In the production of pharmaceuticals, a record for a batch of medication would have details about the ingredients, the formulation, the mixing procedures, the quality checks, and the packaging.
Electronics Industry: The roadmap could include schematics, parts lists, assembly instructions, testing protocols, and packaging specifications for the manufacture of electronic gadgets.
Important Components of Manufacturing Traveler
The components of manufacturing traveler can vary based on the industry, product, and company processes. However, here are some important components commonly found in manufacturing traveler:
1. Product Information:
- Product name, code, or identification number
- Description and specifications of the product
2. Bill of Materials (BOM):
- List of all components, raw materials, and sub-assemblies required
- Part numbers, descriptions, and quantities for each component
3. Routing Instructions:
- The sequence of operations to be performed in the manufacturing process
- Detailed steps for assembly, fabrication, machining, and testing
- Workstation or department where each operation takes place
4. Quality Control Checkpoints:
- Specific checkpoints for quality inspections and tests
- Acceptance criteria for each inspection or test
- Measurements, tolerances, and standards to be met
5. Materials and Tools List:
- List of tools, equipment, and materials needed for each operation
- Special instructions for tooling setup and maintenance
6. Work Instructions:
- Detailed step-by-step instructions for each operation
- Illustrations, diagrams, or photographs to clarify procedures
- Safety precautions and guidelines
7. Process Parameters:
- Parameters such as temperature, pressure, speed, and settings for machinery
- Ensure consistent production and product quality
8. Testing and Inspection Procedures:
- Specific procedures for testing and inspecting product components or assemblies
- Instructions for recording results and deviations
9. Approvals and Signatures:
- Spaces for authorized personnel to sign off on completed operations
- Confirmation of quality checks and inspections
10. Revision History:
- Record all changes made to the manufacturing traveler
- Dates, reasons, and authorizations for revisions
11. Packaging and Shipping Instructions:
- Instructions for packaging, labeling, and preparing the product for shipping
- Addresses, shipping methods, and handling instructions
12. Notes and Comments:
- Space for workers to add comments or notes related to the process
- Issues, challenges, or suggestions for improvement
13. Production Dates and Times:
- Date and time stamps for each operation’s start and completion
- Help in tracking production progress and identifying delays
14. Compliance and Regulatory Information:
- Information regarding regulatory standards, certifications, and compliance requirements
- Documentation to prove adherence to industry standards
15. Traceability and Batch Information:
- Information related to batch or lot numbers for traceability purposes
- Ensures transparency and accountability in case of recalls or quality issues
Storing Manufacturing Traveler – Problems and Solution
Storing manufacturing traveler on regular cloud storage solutions might seem convenient, but it can lead to several significant challenges and limitations. These issues can hinder efficient operations, compromise product quality, and create compliance risks. Here’s a closer look at the problems often faced when using regular cloud storage for manufacturing traveler:
1. Lack of Workflow Integration:
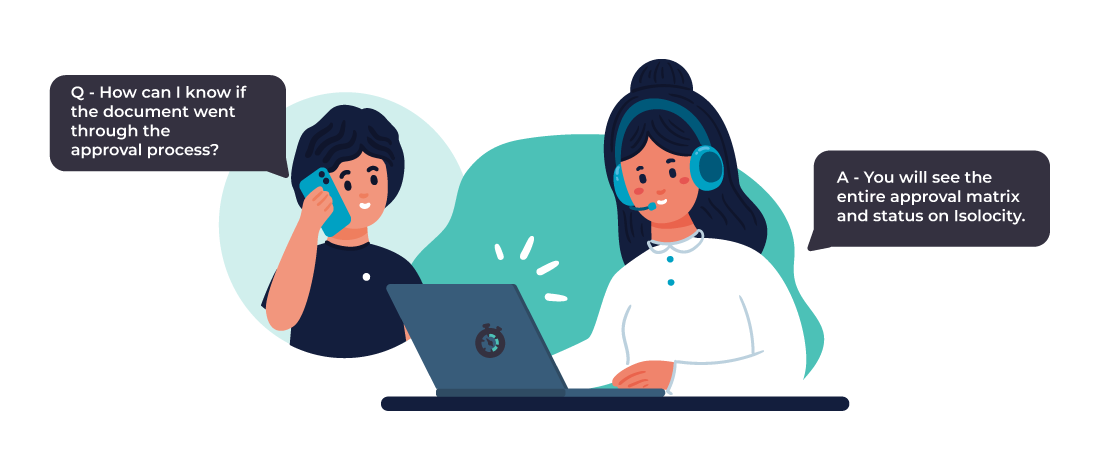
Regular cloud storage lacks the specialized workflow features needed for managing manufacturing processes. Manufacturing traveler involves multiple stages of review, approval, and collaboration. Without dedicated workflow automation, it becomes cumbersome to ensure proper sequencing and accountability.
2. Limited Version Control:
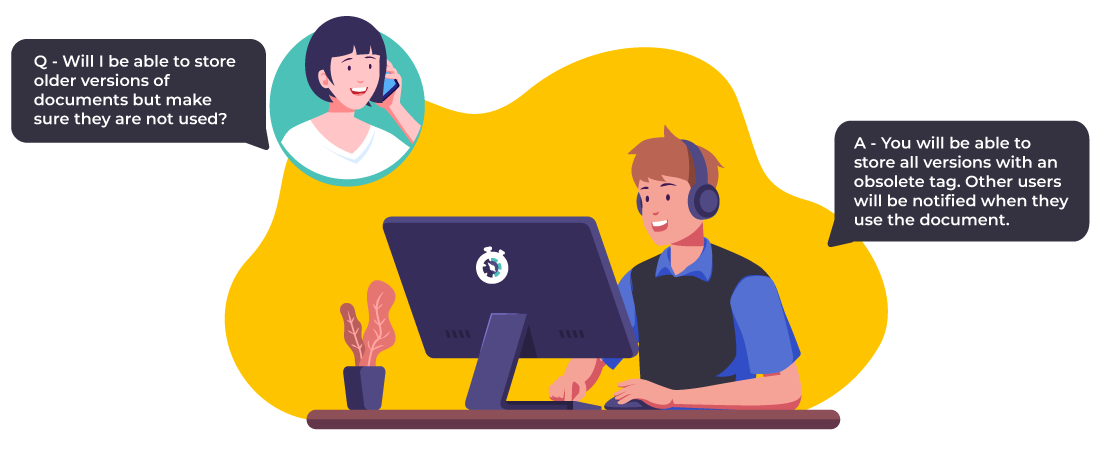
Manufacturing traveler undergoes frequent revisions, and maintaining accurate version control is essential. Regular cloud storage might have basic versioning, but it often lacks advanced capabilities such as side-by-side comparisons, detailed revision histories, and the ability to revert to specific versions.
3. Inadequate Metadata and Categorization:
Manufacturing traveler often requires specific metadata and attributes for categorization and easy retrieval. Regular cloud storage solutions may offer limited customization options, making it challenging to organize and search for documents based on manufacturing-specific criteria.
4. Security and Access Control Challenges:
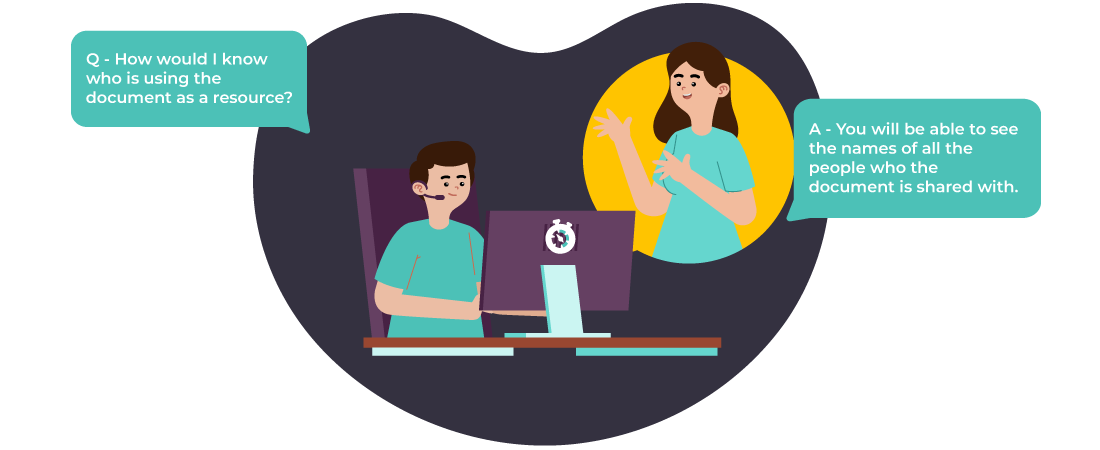
Manufacturing traveler contains sensitive information, and ensuring proper access control is critical. Regular cloud storage might not offer granular permission settings needed to restrict access to authorized personnel only. This can lead to unauthorized modifications or leaks of confidential data.
5. Compliance Risks:
Industries like manufacturing often operate under strict regulatory requirements. Regular cloud storage solutions may lack compliance features such as audit trails, electronic signatures, and validation records. This can jeopardize adherence to regulations and hinder successful audits.
6. Document Linking and Contextualization:
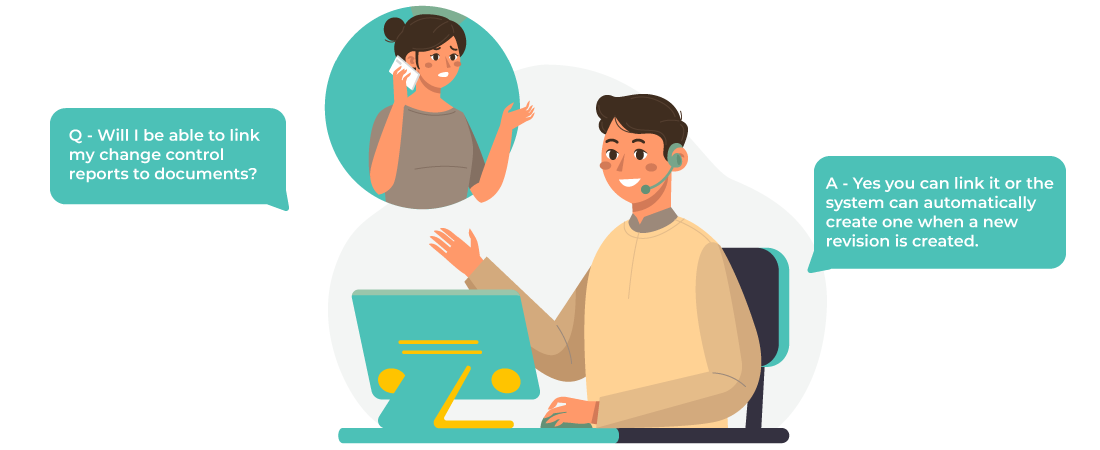
Manufacturing traveler often references related documents, such as specifications, quality control records, and schematics. Regular cloud storage may not provide the ability to establish these links, making it harder for users to understand the context and make informed decisions.
7. Limited Integration with Manufacturing Systems:
Manufacturing processes involve multiple interconnected systems like ERP, QMS, and production control tools. Regular cloud storage typically lacks the integration capabilities required to sync data between these systems, leading to data duplication and inefficiencies.
8. Complex Document Lifecycle Management:
Manufacturing traveler has a lifecycle from creation to archival. Regular cloud storage solutions lack dedicated features for managing this lifecycle effectively, making it difficult to ensure proper updates, archiving, and disposal of documents.
9. Collaboration Challenges:
Manufacturing often involves cross-functional collaboration. Regular cloud storage might lack real-time collaboration features, making it hard for teams to work simultaneously on documents and communicate effectively.
10. Scalability and Performance Concerns:
As manufacturing operations grow, the volume of documents and users increases. Regular cloud storage might face scalability and performance limitations, leading to slower document retrieval and potential disruptions.
Using document management software effectively resolves the challenges posed by regular cloud storage for managing manufacturing traveler.
It offers automated workflows, robust version control, tailored metadata, granular access control, compliance features, document linking, system integration, comprehensive lifecycle management, seamless collaboration, and scalability, all of which are crucial for efficient and compliant manufacturing operations. Isolocity now offers a standalone document management software module, so if you don’t need the entire QMS and require only the document management module, that is possible with Isolocity. You can check the pricing on our pricing page.