In the field of quality management, achieving customer satisfaction is of utmost importance. However, to get the solution, one has to know the problem, and therefore, customer observation is of such high importance. But what are the keys to customer observation? In this blog, we will cover all the important aspects of customer observation, including the needs, strategies, and techniques. We will also discuss one such technique (NPS) in detail.
In addition to reading, you can watch this blog about Customer Observation too!
The Importance of Customer Observation
The compass that directs quality management initiatives is customer observation, which is actively tracking and examining consumer comments and behavior. This is why it is essential:
Understanding of Customer Needs:
Successful customer observation gives priceless information about client preferences, problems, and expectations. Therefore, manufacturing firms can better serve their customers by understanding what they really want from their products and services.
Quality Improvement:
Continuous improvement is the cornerstone of quality management. Customer observation provides data on product defects, failures, or service issues, allowing companies to make data-driven improvements and reduce defects.
Competitive Advantage:
In today’s fiercely competitive market, customer satisfaction sets companies apart. Hence companies that excel in customer observation can identify market trends and stay ahead of the competition.
Loyalty and Retention:
Satisfied customers are more likely to become loyal customers. Therefore by addressing customer concerns promptly and effectively, manufacturing companies can increase customer retention rates and foster brand loyalty.
Risk Mitigation:
Identifying and rectifying issues early on can prevent costly recalls, legal disputes, and damage to a company’s reputation. Customer observation is a proactive way to mitigate such risks.
Key Strategies for Effective Customer Observation
Quality Management Software:
In the modern age, technology is indispensable. When it comes to customer observation with the intent of improving customer satisfaction, quality management software with cutting-edge technologies should definitely be considered that can help manufacturing companies stay compliant with all the governing regulations. Additionally, it has the capability of tracking and analyzing various data that can give insight into the customer.
Multi-Channel Feedback:
Gather feedback from various touchpoints, including surveys, social media, customer support interactions, and online reviews. It is important because a multi-channel approach provides a comprehensive view of customer sentiment.
Data Integration:
Integrate customer data with quality management systems to correlate customer feedback with product and process data. Hence this holistic view helps in identifying the root causes of issues.
Proactive Monitoring:
Proactive monitoring allows for swift responses to emerging issues. Therefore implementing automated alert systems to detect anomalies and customer dissatisfaction trends in real time can be very effective.
Cross-functional collaboration:
Foster collaboration between quality management, product development, and customer support teams. Because sharing ideas and working together on answers can help people solve problems better.
Benchmarking:
Compare customer satisfaction metrics against industry benchmarks and competitors. Because this helps in setting realistic goals and identifying areas for improvement.
Customer Journey Mapping:
Map out the entire customer journey to pinpoint critical touchpoints and moments of truth. Hence understanding these stages helps in focusing observation efforts effectively.
Customer Observation Techniques
Let’s discuss a few customer observation techniques that manufacturing companies widely use.
Questionnaires and Surveys
Customers’ experiences, degrees of happiness, and preferred products/services are frequently gathered through online surveys and paper questionnaires.
Using Focus Groups
Small groups of customers participate in focus groups where they talk about the company’s goods or services. These regulated dialogues might give qualitative information about the preferences and opinions of customers.
Customer feedback forms
To encourage customers to actively offer feedback and suggestions, businesses frequently include feedback forms with their goods and services.
Complaint Tracking and Analysis (CTA)
Recurring problems can be found and areas for improvement can be found by tracking and investigating consumer complaints.
Social Media Monitoring (SMM)
Businesses can monitor social media channels for client feedback, reviews, and mentions of their goods or services. Also, automation of this process can be aided by social listening tools. Therefore manual labour can be minimized for this.
Usability Testing
Customers are seen interacting with a product or service during usability testing. This assists in identifying usability problems and areas that require development.
Mystery Shopping
To evaluate the level of service and get first-hand information on client experiences, businesses may use mystery shoppers who act as regular customers.
Customer Observation Panels (COPs)
Companies can communicate with a chosen set of customers frequently to get continuing feedback and suggestions by forming customer panels or advisory groups.
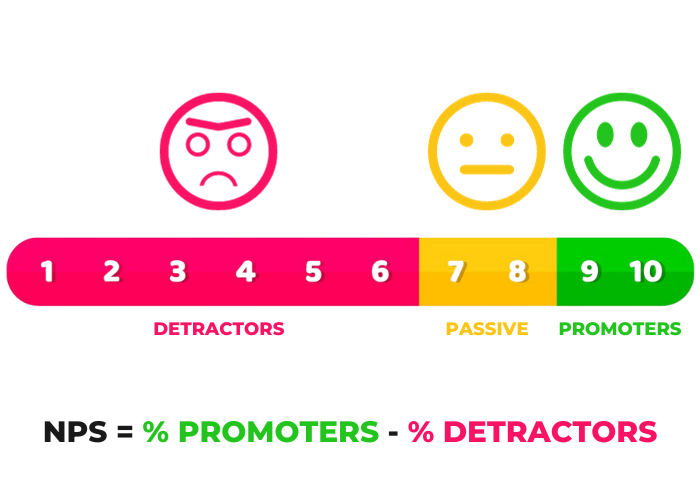
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
By asking respondents how likely they are to tell others about a product or service, NPS surveys gauge client loyalty and satisfaction.
Customer Journey Mapping (CJM)
Identifying pain spots and potential areas for customer experience enhancement can be done by mapping the customer’s journey from first contact to purchase.
Complaint Root Cause Analysis
Manufacturers can address fundamental problems and avoid reoccurring ones by looking into the customer complaints’ root causes.
The Ethnographic Studies
In order to fully understand the customer’s behaviors, requirements, and issues, ethnographic research entails completely integrating researchers into the customer’s environment.
CSI (Customer Satisfaction Index) Surveys:
Customer experience variables including product quality, service, and support are measured as part of CSI surveys to gauge total customer satisfaction.
Customer Observation Technique: Net Promoter Score (NPS)
As it is not possible to discuss all the observation techniques, let’s delve into one technique, Net Promoter Score (NPS), which is the most popular in manufacturing companies. It’s a straightforward yet effective method that can provide valuable insights when applied in companies to enhance customer satisfaction.
Understanding NPS
NPS is based on a single question: “On a scale of 0 to 10, how likely are you to recommend our company/product/service to a friend or colleague?” Based on their responses, customers are classified into three categories:
- Promoters (score 9-10): These are highly satisfied customers who are likely to be loyal and advocate for your brand.
- Passives (score 7-8): These customers are satisfied but not enthusiastic. They are susceptible to competitive offers and may not actively promote your brand.
- Detractors (score 0-6): Detractors are dissatisfied customers who may actively criticize your company and are at risk of leaving for competitors.
How NPS Data Enhances Customer Satisfaction
Benchmarking and Goal Setting:
Comparing NPS scores with industry benchmarks and competitors’ scores provides context. Companies can set realistic improvement goals and track progress over time.
Segmentation:
Companies can segment NPS data by demographics, geography, or other factors to identify which customer groups are less satisfied. This allows for targeted efforts to improve satisfaction within these segments.
Closing the Feedback Loop:
NPS surveys provide an opportunity to follow up with customers. Companies can reach out to detractors to understand their concerns better and take steps to rectify issues, potentially turning them into promoters.
Employee Engagement:
Happy employees often lead to satisfied customers. Hence companies can use NPS data to identify areas where employees may need additional training or support to improve customer interactions.
Product and Service Enhancements:
Promoters often provide feedback on what they love about a product or service. So this data can guide product development and service enhancements to meet and exceed customer expectations.
Promoter Activation:
Identifying promoters can lead to opportunities for referral programs, loyalty incentives, or engagement initiatives that harness their positive sentiments and turn them into brand advocates.
Continuous Improvement:
NPS is not a one-time measurement but an ongoing process. Regularly collecting and analyzing NPS data allows companies to adapt to changing customer preferences and evolving market dynamics.
Conclusion
Customer observation is the key to unlocking success. It not only enhances customer satisfaction but also propels companies toward excellence in quality management. It’s a journey worth undertaking, where companies can thrive and build lasting relationships with their customers, ensuring a prosperous future.