What is Electronic Batch Record?
Maintaining a competitive advantage in today’s fast-paced manufacturing industry requires efficiency and precision. The Electronic Batch Record (EBR) system is a technological advancement that has revolutionized the way in which companies manage their manufacturing processes. This blog will delve deeply into the world of EBRs, examining what they are, how they operate, and the numerous benefits they offer to manufacturers. At the conclusion, you will have a thorough comprehension of EBRs and their potential to revolutionize how your organization manages batch records.
Download Isolocity’s Electronic Batch Records Guide

Download For Free
In addition to reading, you can watch this blog about Electronic Batch Records too!
Electronic Batch Records Understanding
Electronic Batch Records (EBRs) are digital systems used throughout the manufacturing process to capture, store, and manage batch-related information. They serve as a comprehensive record of all activities, specifications, and procedures associated with a batch’s production. EBRs offer a centralized, accessible, and highly traceable solution for managing manufacturing data, in contrast to conventional paper-based batch records.
Electronic forms, electronic signatures, automated data capture, workflow management, and integration capabilities are fundamental EBR system components and features. EBRs eliminate the need for manual data entry, thereby assuring accuracy and minimizing the possibility of errors. In addition, they enable real-time data access, which facilitates improved decision-making and prompt interventions in the event of deviations or issues.
Advantages of Electronic Batch Records
Implementing EBR systems affords manufacturers a variety of advantages. Enhanced data precision and integrity is a significant advantage. With EBRs, data is entered digitally, decreasing the likelihood of transcription errors and misinterpretation. Automated data capture eliminates the need for manual data entry, thereby assuring consistency and dependability.
EBRs also offer crucial advantages such as real-time data access and visibility. Manufacturing stakeholders have access to up-to-date batch status, progress, and quality metric information. This transparency enables improved coordination, proactive decision-making, and timely adjustments to manufacturing processes.
The streamlined workflows and automated processes of EBRs result in increased productivity and efficiency. With digital records, duties can be assigned, tracked, and completed more efficiently, thereby shortening the overall production cycle. In addition, EBRs facilitate integration with other manufacturing systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES), ensuring data continuity and eradicating manual data transfers.
Traceability and auditability are indispensable aspects of regulatory conformance in the manufacturing industry. EBRs provide a complete audit trace, documenting all activities and modifications made during the batch production process. This feature simplifies regulatory audits, expedites investigations, and facilitates root cause analysis, thereby ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations.
In addition, EBRs contribute to the reduction of errors and deviations by enforcing standard operating procedures (SOPs) and providing real-time alerts for out-of-specification conditions. By identifying and addressing deviations as soon as possible, manufacturers can reduce waste, rework, and product recalls, saving both time and resources.
Implementing Electronic Batch Records Successfully
To ensure a smooth transition, implementing EBRs requires meticulous planning and execution. For a successful implementation, organizations need to consider the following steps:
- Assess your organization’s batch record management demands and specifications.
- Identify the EBR system that aligns with your manufacturing processes and regulatory compliance requirements.
- Provide extensive training and change management initiatives to assist employees in adapting to the new system.
- Develop comprehensive data migration and validation strategies to facilitate a seamless transition from paper-based to electronic record formats.
- Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess the success and efficacy of the EBR system.
- Case studies of businesses that have effectively implemented EBRs can provide invaluable insight into best practices and lessons learned. These real-world examples illustrate the transformative effect of EBRs on manufacturing operations, highlighting enhanced productivity, compliance, and overall performance.
How Does an Electronic Batch Records Software Help in Automation?
Electronic batch records software can automate a large number of manual duties and make life much simpler. The features may differ from program to program. Here are some examples from our software that we believe should be present in all effective electronic batch records software. If not, we recommend revising the project’s scope and evaluating alternatives.
Automatic Real-time Calculations
A good electronic batch records software should calculate your inventory automatically using shipping and receiving in your system. Additionally, real-time calculations and updates should all be directly accessible within the software.
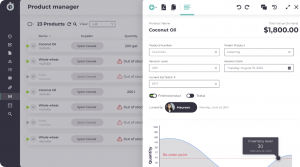
Easily Track Inventory Changes
You should be able to visualize your inventory levels in one click. In addition to viewing you should be able to download your inventory data in a variety of formats. Analysis and audits should also be done in a cinch.
Get Notified When It’s Time to Reorder
A good EBR should notify you when finished goods are too low for shipment, automatically calculate inventory, and tell you when to reorder.
Restock with ease
You should be able to receive raw materials and complete finished goods with ease. The system should update inventory levels the minute you complete any type of inspection.
Challenges of Implementing Electronic Batch Records
While implementing Electronic Batch Records (EBRs) in a production setting can have a positive impact, there are also some drawbacks. For a successful shift from conventional paper-based systems to digital record-keeping, certain obstacles must be overcome. Let’s get into greater detail about the main issues:
Resistance to Change
Employee and stakeholder resistance to change is one of the most frequent obstacles to the adoption of Electronic Batch Records Software. Long-standing paper-based procedures heavily engrain the firm culture, posing challenges for employees in adopting new technologies. The new system’s complexity may put employees off, make them doubt their ability to use technology, or simply lead them to prefer the familiarity of paper records.
Solution:
Organizations should give change management activities a top priority in order to combat the opposition. To acquaint personnel with the EBR system, offer thorough training programs and workshops. Engage important parties right away, highlighting the advantages of EBRs and including them in the decision-making process. Be clear in your explanation of the new system’s goals, benefits, and potential upgrades.
Data Security Concerns
The transition from paper records to digital records may cause data security and integrity issues. Manufacturers may be especially vigilant about the security of electronic systems if they deal with sensitive information, such as intellectual property or data on regulatory compliance.
Solution
To protect sensitive data, adopt strong data security procedures. Implement user authentication methods, access controls, and encryption protocols. Maintain security procedures and update them frequently to keep on top of emerging risks. Confidence in data safety can be increased by investing in secure cloud-based solutions or on-premises servers with robust security measures.
Infrastructure and Initial Investment
There must be an initial investment made in hardware, software, and training in order to implement an EBR system. This investment might raise some questions, especially for industrial companies with lesser budgets.
Solution
To evaluate the long-term benefits of adopting an EBR, perform a cost-benefit analysis. Even while the initial expenses can seem high, they may eventually be outweighed by potential time, resource, and compliance benefits. Consider cloud-based EBR systems to reduce the requirement for pricey infrastructure and look for scalable solutions that can scale with the organization. Isolocity customers have typically seen a return of 500% for the amount they invest with the system.
Data Migration and Validation
When moving paper-based records to digital formats, careful data migration and validation are required. It might be a challenging task to guarantee that all current records are accurately moved to the new system without data loss or corruption.
Solution
Construct a thorough data migration strategy that covers data cleaning, mapping, and validation. Engage knowledgeable IT staff or consultants to help with the migration process. Before launching the EBR system, carry out extensive testing to confirm the consistency and quality of the data.
User Adoption
Even with the best EBR system in place, user adoption is essential to the system’s performance. Employee improper usage of the system or insufficient training might result in mistakes and reduce output.
Solution
Make user training a top priority and offer continuing assistance to make sure that staff members are proficient and confident in utilising the EBR programme. Provide practical instruction classes, user manuals, and access to a help desk or support staff to handle any questions or difficulties encountered during deployment.
Regulatory Compliance and Validation
Ensuring that the EBR system conforms to regulatory norms and guidelines is more difficult in sectors with tight regulatory requirements, like the pharmaceutical or food production industries.
Solution
To ensure that the EBR system complies with all applicable industry norms and laws, work together with regulatory experts and compliance professionals. To prove the system’s compliance and accuracy, carry out extensive validation processes, including risk assessments and documentation.
Conclusion:
Electronic Batch Records have revolutionized the manufacturing industry by expediting processes, improving data accuracy, and enhancing overall productivity. By adopting EBR systems, manufacturers can surmount the limitations of paper-based batch records and attain new levels of efficiency and compliance. EBRs offer numerous advantages, and businesses that implement these digital record-keeping solutions can position themselves for long-term success in an increasingly competitive market. Embrace the power of Electronic Batch Records to maximize the potential of your manufacturing operations.